Control
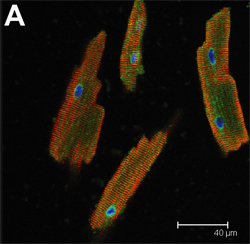
|
Simulated Ischemia
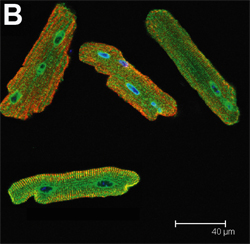
|
| Confocal immunocytofluorescence of adult mouse ventricular myocytes. Endoplasmic reticulum induction by simulated ischemia. Thuerauf D J et al. Circulation Research 2006;99:275-282 |
Integrategrative Approaches to Studies of Heart Disease:
The Glembotski lab uses genomic and proteomic methods to identify molecular signatures of pathology in cellular and animal models of heart disease. Specific gene and protein families of interest are then examined at the cell and molecular levels in order to delineate hypothetical mechanisms of action. Hypotheses concerning mechanisms of action are then interrogated in cultured cell and animal models using targeted molecular gain- and loss-of-function approaches, coupled with functional assessment of the effects of these maneuvers. Subsequent identification of genes and proteins as lead candidates for gene therapy development is followed by development of therapeutic platforms that are tested in animal models of heart disease.
Methods and Models Used in the Lab:
Biochemical, molecular, cellular and physiological methods are used to integrate molecular structure with heart function. In studies of heart disease, the Glembotski lab utilizes cell culture techniques to examine stress signaling in isolated cardiac myocytes, cancer cells and stem cells. Additional methods include novel mechanisms of protein and gene transduction into cultured cells, as well as cells and tissues, in vivo. The development of gene therapies aimed at reducing heart disease, is coupled with assessment of therapeutic outcomes, using state-of-the-art in vivo invasive and non-invasive hemodynamic analyses of heart and cardiovascular system function.
Read more about our research goals
Learn more about Mentorship, Training, and Opportunities in the lab
Learn more about the research conducted in our lab